In SEO, structured data, schema markup, and rich results are related concepts that play a significant role in optimizing websites for search engines.
In easy terms, Google uses structured data to grasp what a webpage is all about and display its content in a more detailed and attractive way in search results also known as SERP’s. This enhanced display is known as a rich result.
While these are different terms & might sound confusing, here is how it works –
Structured data, Schema Mark up & Rich Results – Same thing or different?
- Structured data is the general concept of organizing data in a structured format. Structured data refers to a standardized format used to organize and provide additional context to the content on webpages.
It involves marking up specific elements and attributes on a webpage using structured data formats like JSON-LD, RDFa, or microdata. Structured data helps search engines understand the content better, facilitating improved indexing and presentation of information. - Schema markup is a specific implementation of structured data using the schema.org vocabulary. It uses predefined schemas and properties to tag different types of content on a webpage, such as articles, products, events, recipes, and more.
Schema markup provides explicit instructions to search engines about the meaning and structure of the content, enabling them to display relevant rich results.
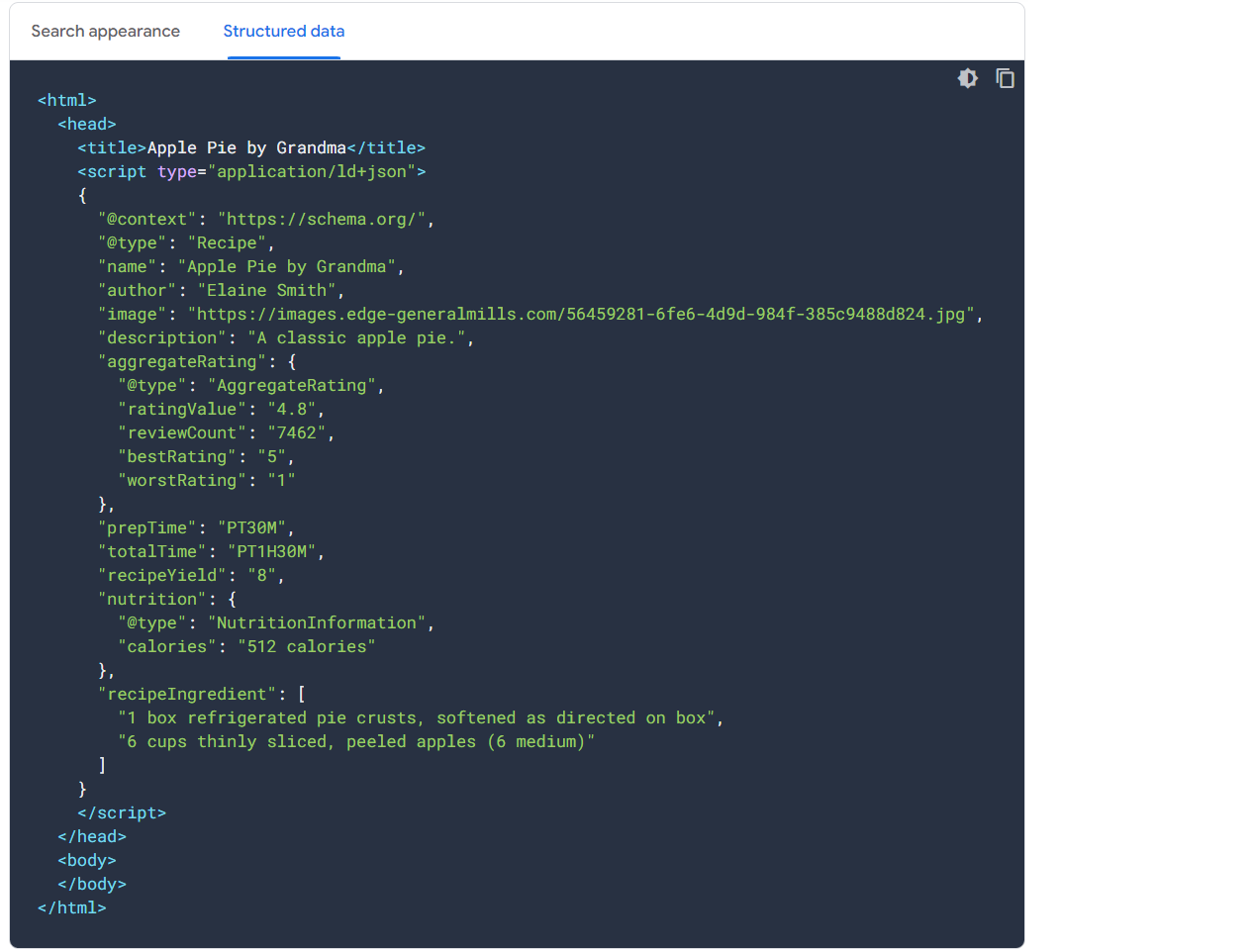
Above Example from Google.com Documentation which shows Structured Data implemented through JSON LD Schema Mark up
- Rich results are the visually enhanced search results that arise from search engines interpreting and presenting structured data or schema markup.
When search engines understand and interpret the structured data on a webpage, they can generate rich results that go beyond traditional blue links.
Rich results can include additional information, images, reviews, ratings, and other elements directly in the search engine results pages (SERPs).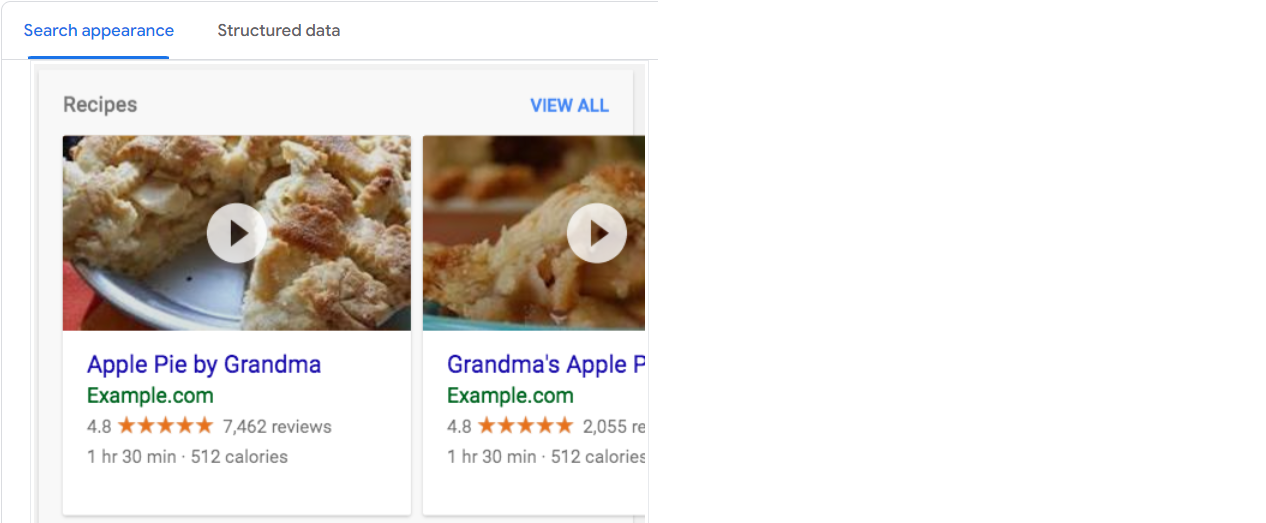
Above image displays how Structured data discussed above appears in Google Search Listings - Implementing structured data through schema markup increases the likelihood of your website being eligible for rich results, ultimately improving your website’s visibility and user engagement in search engine rankings.
Note – As per Google Documentation, Google does not guarantee that your page will appear exactly as shown here, or that any of the views shown will be applied to your page result; Google tries to show the best result for a search request, based on the user’s search history, location, and many other variables.
Most Commonly Seen Rich Results on Google
- Recipe (Recipe, HowTo, ItemList) structured data
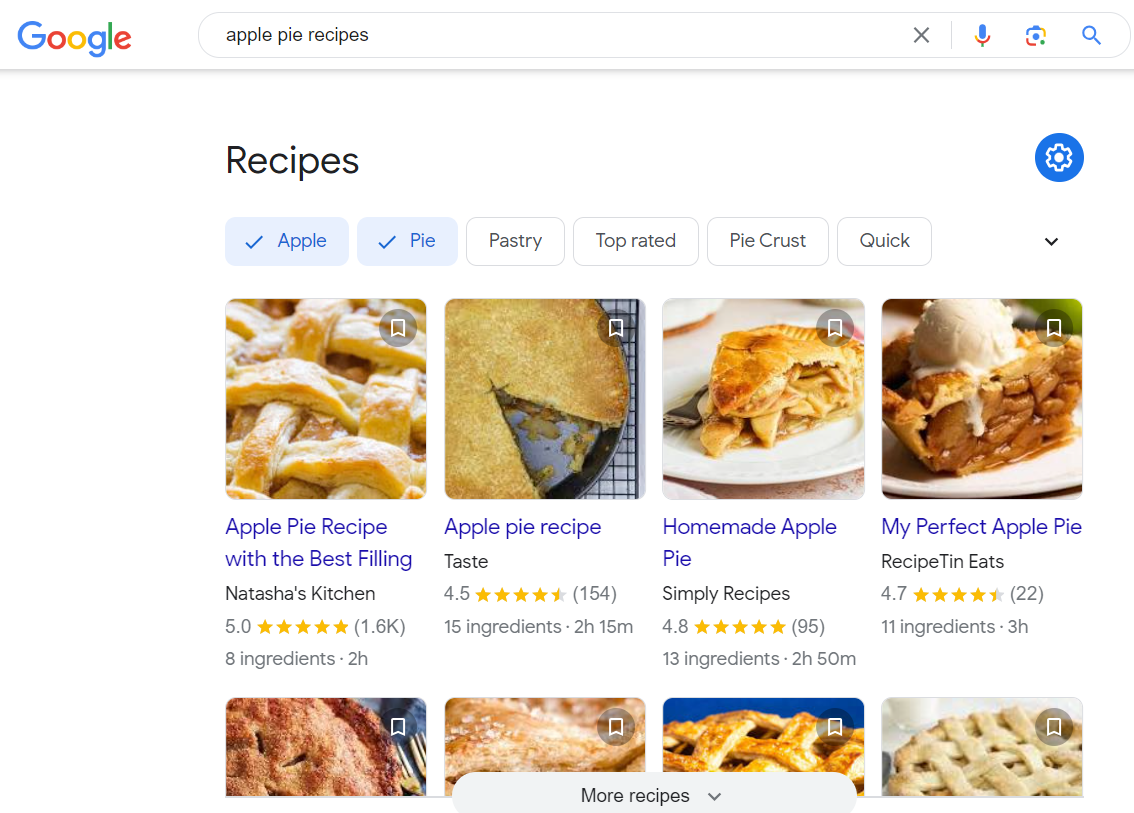
Search Query – Apple Pie Recipe
Link to Google Documentation on Implementation & How it works - Review snippet (Review, AggregateRating) structured data
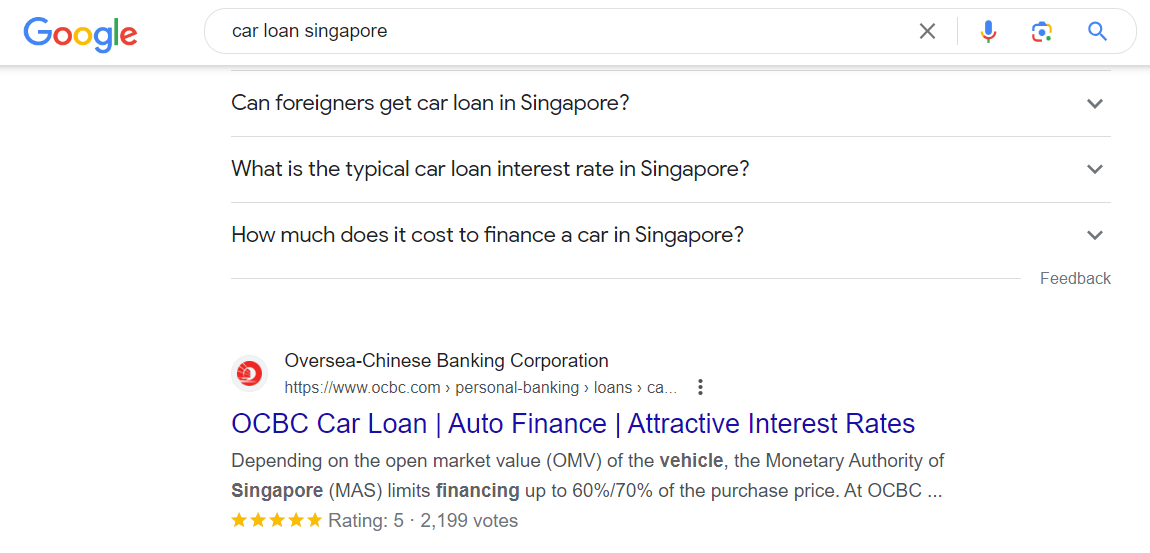
Search Query – Car Loan
Link to Google Documentation on Implementation & How it works
3. FAQ (FAQPage, Question, Answer) structured data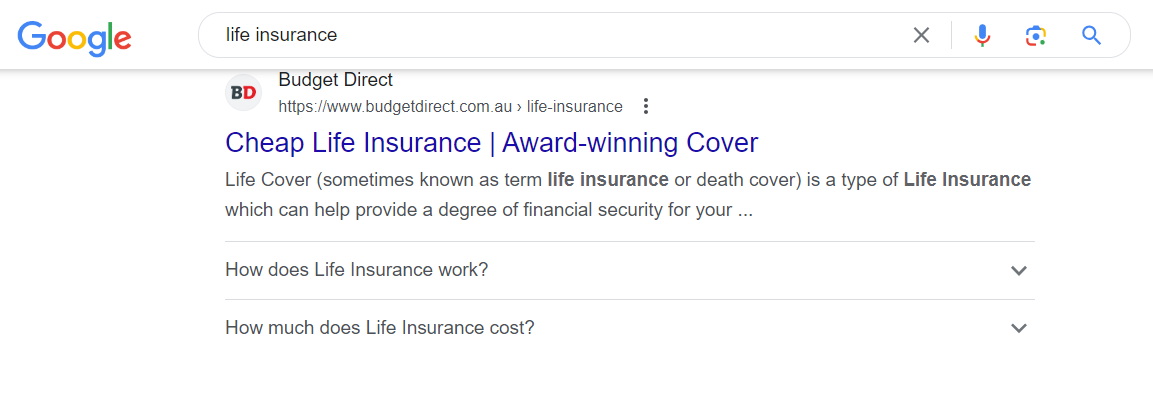
Search Query – Life Insurance
Link to Google Documentation on Implementation & How it works
On 8th August 2023, Google made following statement about reducing the visibility of FAQ and How-to rich results
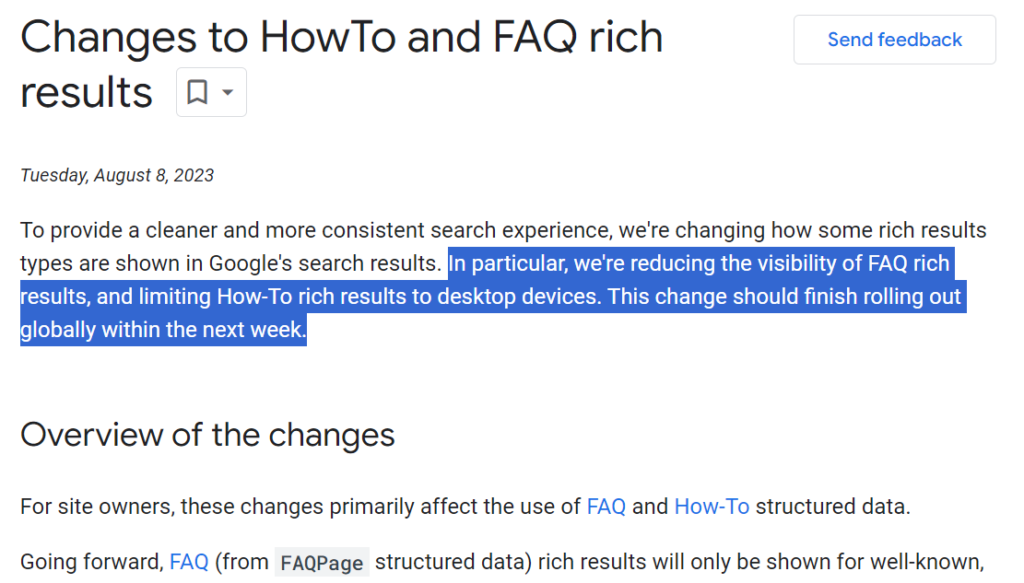
For detailed reading, please visit Changes to FAQ & How-to rich results
4. Sitelinks search box (WebSite) structured data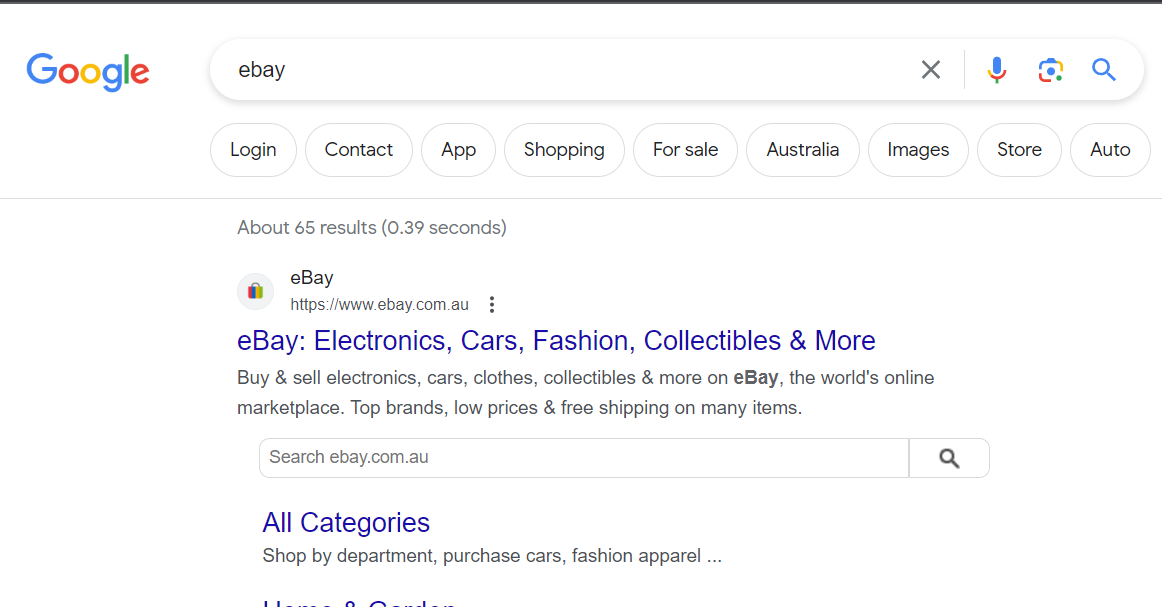
Search Query – eBay
Link to Google Documentation on Implementation & How it works
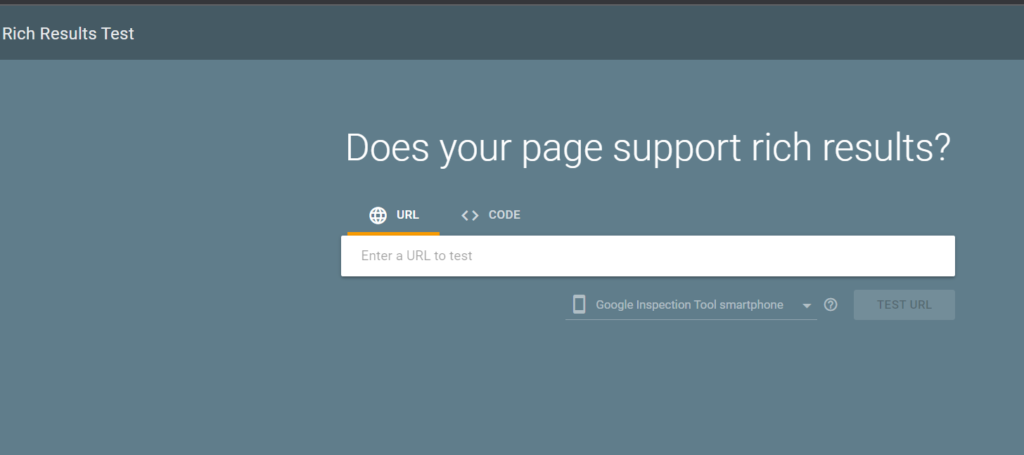
How to check if your page or source code is eligible for rich results?
You can text a publicly accessible page to see which rich results can be generated by the structured data it contains on Google Rich Results Tool
It has 2 options to choose from –
- Enter Page URL
- Code
These are just a few examples of the types of schema markups (we will be adding more examples in the coming days) that search engines commonly display as rich results.
It’s important to implement the relevant schema markup for your content to increase the chances & does not guarantee of your website being featured prominently in search results with enhanced information and visuals.